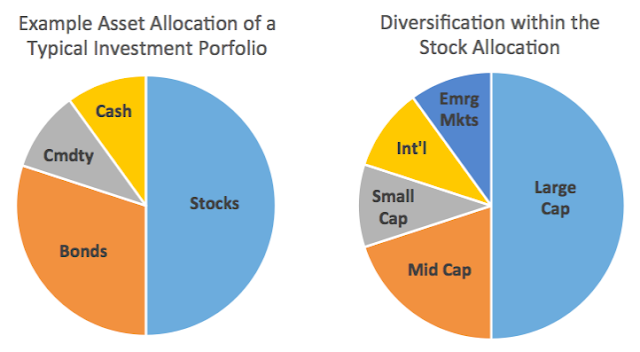
Asset Allocation refers to investing in different categories of investments, called asset classes. That is, we pick which assets we want to have in our portfolio. Generally, investors choose from stocks (equities), bonds (fixed income), cash, commodities and real estate.
Diversification, on the other hand, is the process of balancing these classes – and within these classes – so they offset one another amid ever-changing market conditions.
(Source: Stockcharts.com)
Your asset allocation may represent a diversified portfolio or a
concentrated portfolio, if you are only using a couple of
specific asset classes, then it is probably a concentrated portfolio. The goal of portfolio diversification is to generate the highest possible return for a given level of
risk. A portfolio of all small company stocks may
result in greater returns than a diversified portfolio of stocks, but it
is unlikely to achieve that result without significantly more risk or
volatility.
Asset allocation is a key element of diversification. No asset class is
the top performer each year, so selecting asset classes that are not
well correlated or do not move in the same
direction, makes sense.
Here is an example of a portfolio with asset allocation and diversification:
You may also want to read this article on stockcharts.com for a better understanding of the difference between Asset Allocation and Diversification.
Here is another detailed article- Beginners' Guide to Asset Allocation, Diversification, and Rebalancing I found on SEC's website.


No comments:
Post a Comment